Resonant Frequency Of Patch Antennas
Microstrip Antennas The Patch Antenna. In this section, well discuss the microstrip antenna, which is also commonly referred to as the patch antenna. Note. Ill use the terms microstrip antenna and patch antenna interchangeably. The rectangular patch antenna is analyzed, and what is learned here will be applied to understanding. PIFAs Planar Inverted F Antennas. Rectangular Microstrip Antenna Introduction to Patch Antennas. Microstrip or patch antennas are becoming increasingly useful because they can be printed directly onto a circuit board. Microstrip antennas. Patch antennas are low cost, have a low profile and are easily fabricated. Consider the microstrip antenna shown in Figure 1, fed by a microstrip transmission line. The patch antenna, microstrip transmission line and. Shorting pins used in patch antennas are discussed. These can add a design parameter or degree of freedome that allows the performance to be tuned. The PIFA Planar. The patch is of length L. W, and sitting on top of a substrate some dielectric circuit board of thickness h with. The thickness of the ground plane or of the microstrip is not critically important. Typically the height h is much smaller than the wavelength of operation, but should not be much smaller than 0. Top View of Patch Antennab Side View of Microstrip Antenna. Figure 1. Geometry of Microstrip Patch Antenna. The frequency of operation of the patch antenna of Figure 1 is determined by the length L. Resonant Frequency Of Patch Antennas Design' title='Resonant Frequency Of Patch Antennas Design' />The center frequency will. The above equation says that the microstrip antenna should have a length equal to one half of a wavelength within the dielectric substrate. The width W of the microstrip antenna controls the input impedance. Larger widths also can increase the bandwidth. For a square patch antenna fed in the manner above. Ohms. By increasing the width, the impedance can be reduced. However, to decrease the input impedance. Ohms often requires a very wide patch antenna, which takes up a lot of valuable space. The width further controls the. The normalized radiation pattern is. In the above, k is the free space. The magnitude of the fields, given by. The fields of the microstrip antenna. Figure 2 for WL0. Figure 2. Normalized Radiation Pattern for Microstrip Patch Antenna. The directivity of patch antennas is approximately 5 7 d. B. The fields are linearly polarized, and in the horizontal. Library of Congress CataloginginPublication Data De Los Santos, Hctor J. RF MEMS circuit design for wireless communicationsHctor J. De Los Santos. Mfj Fast Shipping Car Stereo Parts at installer. Receiving only antennas collected in AntennasReceiving at The DXZone. Our brain waves share and are attuned to certain frequencies of the Schumanns resonances, the ELF signals that pulsate between the Earths crust and ionosphere. Figure 1a well see why in the next section. Next well consider more aspects involved in Patch Microstrip antennas. Fringing Fields for Microstrip Antennas. Consider a square patch antenna fed at the end as before in Figure 1a. Assume the substrate is air or styrofoam, with a permittivity equal to 1, and. LW1. 5 meters, so that the patch is to resonate at 1. MHz. The height h is taken to be 3 cm. Resonant Frequency Of Patch Antennas Pdf' title='Resonant Frequency Of Patch Antennas Pdf' />Note that microstrips are usually made for higher frequencies. When matched to a 2. Ohm load, the magnitude of. ANTENNA MAGUS Complete list of Antennas in the database Antenna information Horns, Spirals, patch antennas, wire antennas, reflectors, wideband, high gain, dish. Rectangular Microstrip Antenna. Introduction to Patch Antennas. Microstrip or patch antennas are becoming increasingly useful because they can be printed directly. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation includes theoretical and experimental advances in antennas. Slotted Waveguide Antennas. Unlike wideband antennas like the biquad, slotted waveguides are resonant antennas, and have a relatively narrow operating frequency range. S1. 1 is shown in Figure 3. Figure 3. Magnitude of S1. Frequency for Square Patch Antenna. Some noteworthy observations are apparent from Figure 3. First, the bandwidth of the patch antenna is very small. Rectangular. patch antennas are notoriously narrowband the bandwidth of rectangular microstrip antennas are typically 3. Secondly, the microstrip antenna was designed. MHz, but it is. resonant at approximately 9. MHz. This shift is due to. Hence, when designing a patch antenna it is typically trimmed. Table_2.jpg' alt='Resonant Frequency Of Patch Antennas In Hfss' title='Resonant Frequency Of Patch Antennas In Hfss' />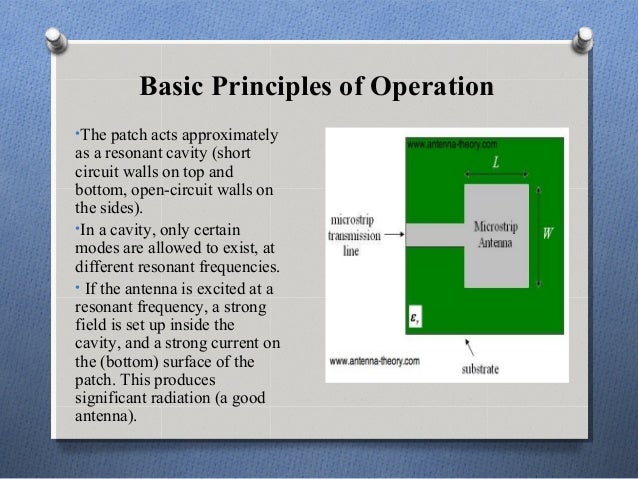 The fringing fields around the antenna can help explain why the microstrip antenna radiates. Consider the side view of. Figure 4. Note that since the current at the end of the patch is zero open circuit end, the. This low current value. Since the patch antenna can be viewed as an open circuited transmission line, the voltage reflection coefficient. When this occurs, the voltage and current are out of phase. Hence, at the end of the patch the voltage. V volts. At the start of the patch antenna a half wavelength away, the voltage must be at minimum V Volts. Hence, the fields underneath the patch will resemble that of Figure 4, which roughly displays the fringing of the fields. Figure 4. Side view of patch antenna with E fields shown underneath. It is the fringing fields that are responsible for the radiation. Note that the fringing fields near the surface. Hence, the fringing E fields on the edge of the microstrip antenna. This paragraph is critical to understanding the patch antenna. The current adds up in. This also explains why the microstrip antenna radiates but the microstrip transmission line. The microstrip antennas radiation arises from the fringing fields, which are due to the advantageous voltage. The patch antenna is therefore a. As a side note, the smaller is. Therefore, using a smaller permittivity for the substrate yields. In contrast, when making a microstrip transmission line where no power is to be radiated. This is one of the trade offs in patch antenna design. There have been research papers. Next, well look at alternative methods of feeding the microstrip antenna connecting the antenna to the receiver or transmitter. Next Feeding Methods for Patch Antennas. Top Introduction to Microstrip Antennas. Antennas List. Antenna Theory Page. This page on microstrip antennas and patch antennas is copyrighted. No portion can be reproduced except by permission. Copyright 2. 01. 1 2. Patch antennas, microstrip antennas. Patch antenna Wikipedia. A patch antenna also known as a rectangular microstrip antenna is a type of radio antenna with a low profile, which can be mounted on a flat surface. It consists of a flat rectangular sheet or patch of metal, mounted over a larger sheet of metal called a ground plane. They are the original type of microstrip antenna described by Howell in 1. The radiation mechanism arises from discontinuities at each truncated edge of the microstrip transmission line. The radiation at the edges causes the antenna to act slightly larger electrically than its physical dimensions, so in order for the antenna to be resonant, a length of microstrip transmission line slightly shorter than one half the wavelength at the frequency is used. The patch antenna is mainly practical at microwave frequencies, at which wavelengths are short enough that the patches are conveniently small. It is widely used in portable wireless devices because of the ease of fabricating it on printed circuit boards. Multiple patch antennas on the same substrate see image called microstrip antennas, can be used to make high gainarray antennas, and phased arrays in which the beam can be electronically steered. A variant of the patch antenna commonly used in mobile phones is the shorted patch antenna, or planar inverted F antenna PIFA. In this antenna, one corner of the patch or sometimes one edge is grounded with a ground pin. This variant has better matching than the standard patch. Another variant of patch antenna with the partially etched ground plane, also known as printed monopole antenna, is a very versatile antenna for dual band operations 3. ReferenceseditMicrostrip Antennas, IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation, Williamsburg Virginia, 1. Radiation from Microstrip Radiators, IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, April 1. Vol. 1. 7, No. 4 pp. J. R. Panda, Rakhesh Singh Kshetrimayum, A Printed 2. GHz5. 8 GHz Dual band Monopole Antenna with a Protruding Stub in the Ground Plane for WLAN and RFID Applications, Progress In Electromagnetics Research, vol. See alsoeditExternal linksedit. Vegas Movie Studio Platinum 8.0 Series Keygen.
The fringing fields around the antenna can help explain why the microstrip antenna radiates. Consider the side view of. Figure 4. Note that since the current at the end of the patch is zero open circuit end, the. This low current value. Since the patch antenna can be viewed as an open circuited transmission line, the voltage reflection coefficient. When this occurs, the voltage and current are out of phase. Hence, at the end of the patch the voltage. V volts. At the start of the patch antenna a half wavelength away, the voltage must be at minimum V Volts. Hence, the fields underneath the patch will resemble that of Figure 4, which roughly displays the fringing of the fields. Figure 4. Side view of patch antenna with E fields shown underneath. It is the fringing fields that are responsible for the radiation. Note that the fringing fields near the surface. Hence, the fringing E fields on the edge of the microstrip antenna. This paragraph is critical to understanding the patch antenna. The current adds up in. This also explains why the microstrip antenna radiates but the microstrip transmission line. The microstrip antennas radiation arises from the fringing fields, which are due to the advantageous voltage. The patch antenna is therefore a. As a side note, the smaller is. Therefore, using a smaller permittivity for the substrate yields. In contrast, when making a microstrip transmission line where no power is to be radiated. This is one of the trade offs in patch antenna design. There have been research papers. Next, well look at alternative methods of feeding the microstrip antenna connecting the antenna to the receiver or transmitter. Next Feeding Methods for Patch Antennas. Top Introduction to Microstrip Antennas. Antennas List. Antenna Theory Page. This page on microstrip antennas and patch antennas is copyrighted. No portion can be reproduced except by permission. Copyright 2. 01. 1 2. Patch antennas, microstrip antennas. Patch antenna Wikipedia. A patch antenna also known as a rectangular microstrip antenna is a type of radio antenna with a low profile, which can be mounted on a flat surface. It consists of a flat rectangular sheet or patch of metal, mounted over a larger sheet of metal called a ground plane. They are the original type of microstrip antenna described by Howell in 1. The radiation mechanism arises from discontinuities at each truncated edge of the microstrip transmission line. The radiation at the edges causes the antenna to act slightly larger electrically than its physical dimensions, so in order for the antenna to be resonant, a length of microstrip transmission line slightly shorter than one half the wavelength at the frequency is used. The patch antenna is mainly practical at microwave frequencies, at which wavelengths are short enough that the patches are conveniently small. It is widely used in portable wireless devices because of the ease of fabricating it on printed circuit boards. Multiple patch antennas on the same substrate see image called microstrip antennas, can be used to make high gainarray antennas, and phased arrays in which the beam can be electronically steered. A variant of the patch antenna commonly used in mobile phones is the shorted patch antenna, or planar inverted F antenna PIFA. In this antenna, one corner of the patch or sometimes one edge is grounded with a ground pin. This variant has better matching than the standard patch. Another variant of patch antenna with the partially etched ground plane, also known as printed monopole antenna, is a very versatile antenna for dual band operations 3. ReferenceseditMicrostrip Antennas, IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation, Williamsburg Virginia, 1. Radiation from Microstrip Radiators, IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, April 1. Vol. 1. 7, No. 4 pp. J. R. Panda, Rakhesh Singh Kshetrimayum, A Printed 2. GHz5. 8 GHz Dual band Monopole Antenna with a Protruding Stub in the Ground Plane for WLAN and RFID Applications, Progress In Electromagnetics Research, vol. See alsoeditExternal linksedit. Vegas Movie Studio Platinum 8.0 Series Keygen.
